Introduction: Exploring the Wonders of the Indus Valley Civilization
Have you ever wondered about the ancient civilizations that shaped the world we live in today? One such fascinating culture is the Indus Valley Civilization, often regarded as one of the most advanced societies of its time. Spanning across the vast territories of present-day India, Pakistan, and parts of Afghanistan, this civilization offers a remarkable glimpse into early urbanization, sophisticated architecture, and artistry.
From its meticulously planned cities like Mohenjo-Daro and Harappa to its intricate bead-making industries and fascinating animal motifs found on seals, the Indus Valley holds secrets that continue to intrigue historians, archaeologists, and enthusiasts. But what makes it truly captivating? Is it the advanced drainage systems and town planning or the rich material culture, including pottery, jewelry, and copper tools?
In this post, we’ll delve into the history and key features of the Indus Valley Civilization—uncovering how its art, architecture, and innovative systems influenced the world and set the foundation for future urban societies. From the famous dancing girl sculpture to the enigmatic Harappan script, we’ll explore how the civilization thrived and what we can learn from their advancements. Let’s take a journey back in time to uncover the legacy of one of humanity’s greatest ancient civilizations.
The Advanced Urban Planning of the Indus Valley Civilization
What made the Indus Valley Civilization stand out from other ancient cultures? One of its most impressive achievements was undoubtedly its urban planning. Long before the rise of other major civilizations, the people of the Indus Valley were creating meticulously designed cities that displayed an extraordinary understanding of engineering, sanitation, and layout.
City Layout: A Masterclass in Urban Design
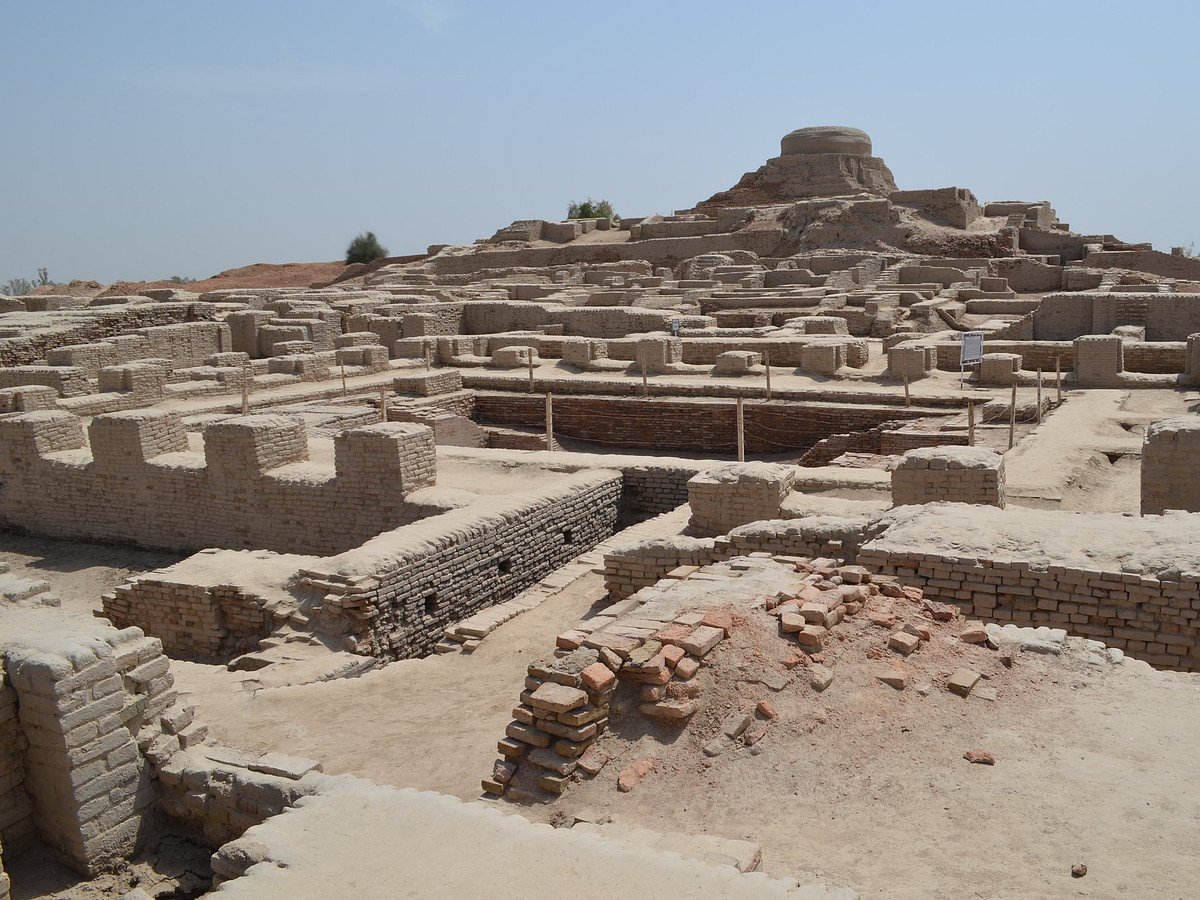
Unlike many ancient settlements that grew haphazardly, cities like Mohenjo-Daro and Harappa were built with clear planning and organization. These cities followed a grid pattern, with streets laid out at right angles to each other, creating a neat and orderly structure. This wasn’t just for aesthetic appeal; it was a deliberate design that promoted efficiency and functionality.
The cities were divided into two main sections: the citadel and the lower town. The citadel was often elevated and housed important buildings like granaries, baths, and large public structures, suggesting a well-organized society with an emphasis on governance and social organization.
Here’s what stood out in their urban design:
- Grid Layout: Streets were aligned in a precise north-south and east-west grid, much like modern urban planning.
- Wide Roads: Roads were broad and spacious, allowing easy movement of people and goods throughout the city.
- Building Materials: Most structures were built with standardized fired bricks, ensuring consistency in construction.
Innovative Drainage Systems: Ahead of Their Time
Have you ever walked through a city and thought, “I wish the sewage system was more efficient”? The residents of the Indus Valley likely never had that problem. One of the most extraordinary features of their urban planning was the advanced drainage systems. Every house in Mohenjo-Daro had its own private toilet connected to the public sewage system.
Key features of their drainage system included:
- Covered Drains: Streets were equipped with large, covered drains to carry away waste, preventing any contamination of the water supply.
- Well-Planned Water Supply: Houses had access to wells, which were often located at strategic points in the city, ensuring easy access to water for daily use.
- Separation of Waste: The drains were cleverly designed to separate clean water from waste, reflecting a clear understanding of hygiene and public health.
Why Did This Matter?
So, why did these advancements in urban planning matter so much? It wasn’t just about creating beautiful cities—it was about sustainability, cleanliness, and creating environments where people could thrive. The cities were designed to maximize resources, maintain hygiene, and ensure the comfort and safety of the inhabitants. Their foresight in city design allowed them to manage dense populations and engage in trade with neighboring regions while maintaining a high standard of living.
When you think about ancient civilizations, you might imagine structures like the Great Pyramids or the Colosseum. But the Indus Valley Civilization’s innovations in urban planning show us that their true genius lay in creating sustainable, efficient living spaces for their people—long before the rise of modern cities.
In fact, many of the urban principles we use today—like grid street planning and wastewater management—can trace their roots back to this incredible ancient civilization. So, next time you walk through a well-planned city, you might want to thank the Indus Valley for setting the groundwork thousands of years ago.
Conclusion: The Lasting Legacy of the Indus Valley Civilization
As we look back on the remarkable achievements of the Indus Valley Civilization, it’s clear that their contributions go far beyond their time. From the impressive urban planning and advanced drainage systems to the evidence of early trade and sustainable living practices, their legacy continues to shape the way we think about city design and public health.
But here’s the big question: Why does all of this matter to us today? What can we, in our modern world, learn from this ancient civilization?
The answer is simple. The Indus Valley people understood something that many societies still struggle with: the importance of planning and infrastructure in creating thriving, sustainable communities. Whether it’s the efficient use of resources, the emphasis on hygiene, or the careful consideration of urban layouts, their innovations were ahead of their time—and they hold lessons for us today.
As we face challenges like rapid urbanization, climate change, and the need for more sustainable development, the principles of the Indus Valley offer valuable insights. Their focus on organized spaces, sustainability, and communal well-being can inspire modern urban planners, architects, and even individuals who want to live in more balanced and sustainable environments.
So, the next time you walk through a bustling city or think about how your own community could evolve, remember the ingenuity of the Indus Valley Civilization. Their groundbreaking approach to urban planning and sustainability not only shaped their world but continues to influence ours in profound ways.
It’s amazing how something that happened thousands of years ago still speaks to the needs and aspirations of our time, isn’t it?